Impact of Expansionary Fiscal Policy
Definition of expansionary fiscal policy. This involves the government seeking to increase aggregate demand – through higher government spending and/or lower tax.
Expansionary fiscal policy is usually financed by increased government borrowing – and selling bonds to the private sector.
Keynes said expansionary fiscal policy should be used during a recession – when there is unemployment, surplus saving and falling real output. He argued this injection of government spending could stimulate economic activity and get the unemployed resources back into productive use. This enables the economy to recover more quickly than a laissez-faire approach.
Expansionary Fiscal Policy – AD/AS
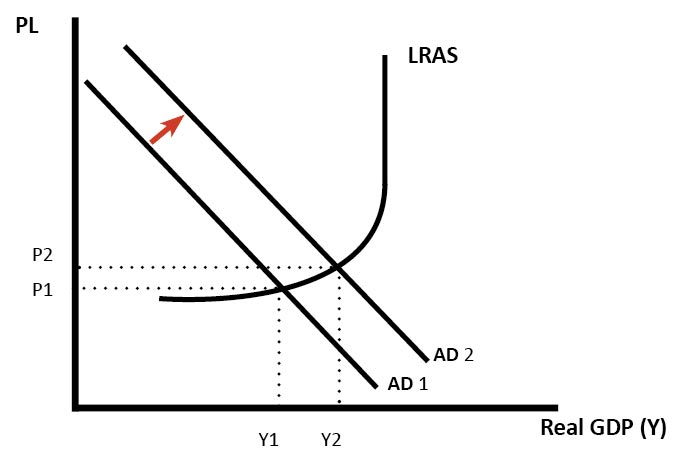
How expansionary fiscal policy works
If the government cut income tax, then this will increase the disposable income of consumers and enable them to increase spending. Higher consumption will increase aggregate demand and this should lead to higher economic growth.
Alternatively, if the government increased investment in public work schemes, this government spending would create jobs, increase incomes and lead to greater aggregate demand.
This injection of money into the economy can also cause a positive multiplier effect. For example, builders who gain a job will also spend more creating jobs elsewhere in the economy. From the government’s initial injection the final increase in real GDP will be more than the initial investment.
Expansionary fiscal policy can also lead to inflation because of the higher demand in the economy.
Paradox of thrift
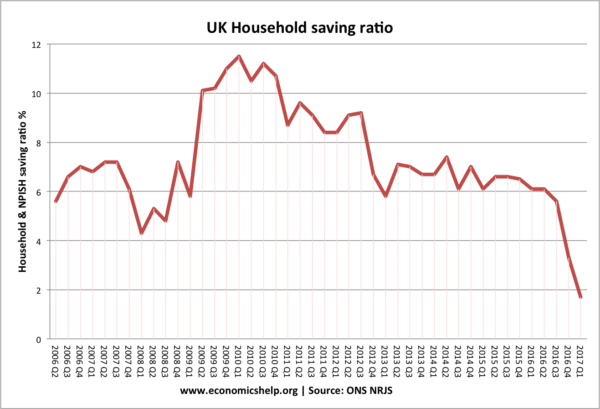
One argument for fiscal policy is that the government spend more to offset the rise in private sector saving and fall in private sector spending.
At the start of the recession in 2009, the saving ratio rose rapidly as consumers cut back on spending. This caused a fall in demand. Fiscal policy can make use of this rise in saving and spend more.
Expansionary fiscal policy and government borrowing
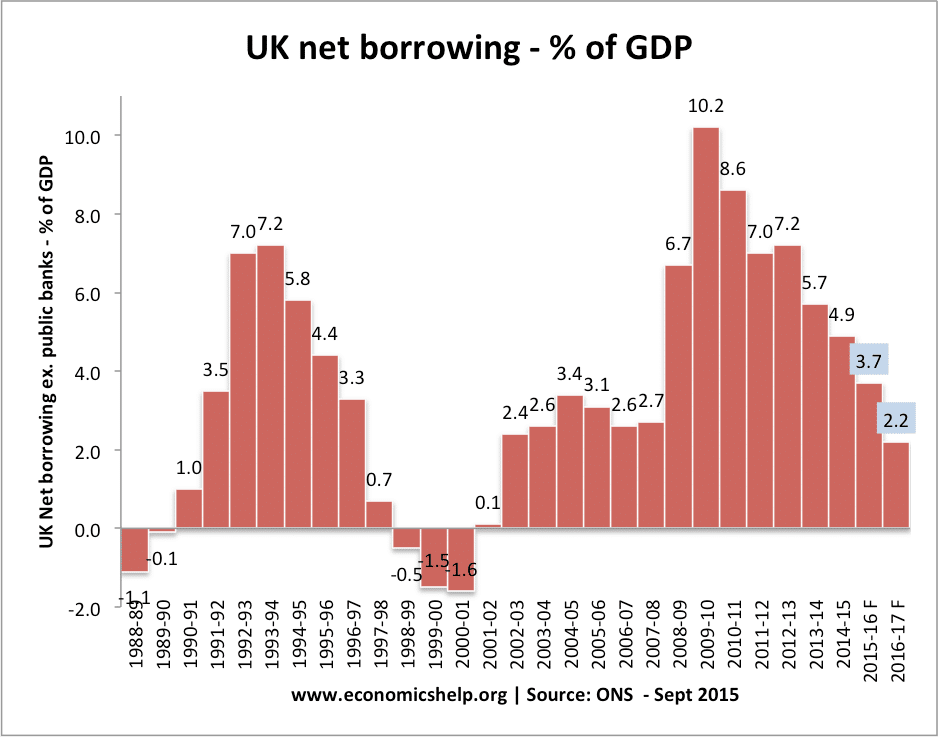
A potential problem of expansionary fiscal policy is that it will lead to an increase in the size of a government’s budget deficit.
Higher borrowing could:
- Financial crowding out. Larger deficits could cause markets to fear debt default and push up interest rates on government debt. (this happened in Eurozone without Central Bank to purchase bonds, but bond yields fell in UK/US due to strong demand for bonds.
- Resource crowding out. If private investors buy government bonds, they have less to use for private sector investment.
Evaluation of expansionary fiscal policy
The impact of expansionary fiscal policy will depend on many factors:
1. What else is happening in the economy?
- Lower income tax may fail to boost AD if we also have falling house prices and low confidence.
- For example in 2008, the US tried to cut taxes; in theory, this lower tax should boost spending. However, the economy was also experiencing falling house prices, lower confidence and a shortage of credit; because of all these factors, expansionary fiscal policy was relatively ineffective in promoting rapid economic growth.
2. Crowding out
- Crowding out occurs when the government spends more, but because they borrow from the private sector, the private sector reduces private sector investment and therefore government spending ‘crowds out’ private sector spending.
- However, in a liquidity trap/recession, private saving rates rise rapidly. Therefore, expansionary fiscal policy helps to offset the rise in private sector saving and injects money into the circular flow and doesn’t cause crowding out.
3. Timing of fiscal policy – amount of spare capacity
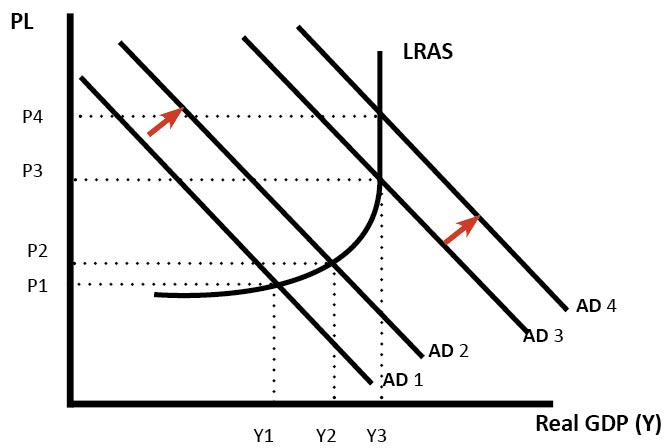
- A key issue of expansionary fiscal policy is the state of the economy. If expansionary fiscal policy is pursued when the economy is close to full capacity (e.g. AD3 to AD4), then the increased government borrowing is likely to cause crowding out and/or contribute to higher inflation – but little increase in real GDP.
- In a deep recession, with spare capacity in the economy, expansionary fiscal policy won’t cause crowding out or inflation. (AD1 to AD2 causes real GDP to rise from Y1 to Y2.)
Supply side effects of fiscal policy
- Lower income tax may increase incentive to work
- Higher government spending on education and training, could increase long-term labour productivity and help the long-term trend rate of economic growth.
- But, also government spending could be inefficient and wasteful – it depends on what the government spends the extra spending on.
Automatic vs Discretionary fiscal policy
- Automatic fiscal stabilisers. In a recession, the government will automatically spend more on unemployment benefits (because more people will be unemployed). Also, in a recession, people pay less income tax (because they earn less)
- Discretionary fiscal stabilisers. This occurs when the government changes tax rates or increases/decreases level of government spending
Different views on fiscal policy
- Keynesians argue that fiscal policy should be pursued during a recession – when there is a rise in demand-deficient unemployment and surplus savings. Keynesians argue there will not be crowding out if the economy is below full capacity.
- Monetarists tend to be more critical of fiscal policy arguing that higher government borrowing is likely to cause crowding out – higher government spending only leads to a fall in private sector spending.
- Modern Monetary Theory (MMT). This argues expansionary fiscal policy can be financed by printing money – so long as inflation is kept within a suitable target.
- Ricardian equivalence. This argues that expansionary fiscal policy doesn’t cause any increase in demand because if consumers receive a tax cut now, then they expect taxes to rise in the future to pay off the rise in government debt.
Related
- Does Fiscal Policy solve unemployment?
- Monetary vs fiscal policy
- Fiscal Policy





